UNIT NO.6
Chemical Bond
(Solved Exercise)
6.2 Define the following and explain with examples.
1. Valency
The combining capacity of atoms with other atoms is called valency.
Example: Hydrogen atom can donate one electron or gains one electron to get its electronic configuration stable. As It can donate one
electron, it has one unit capacity to be combined with another atom. Hence, its valency is one (1).
2. Ion
The charged particle (atom or group of atoms) is called ion.
Example:


3. Formula
A symbolic representation of one molecule of an element or a compound is called its formula.
Example: H2O is the chemical formula of water. It 2 shows that each molecule of water contains two atoms of hydrogen and one atom of oxygen chemically combined together.
4. Bond
A chemical bond is a force of attraction between atoms that holds them together in a substance.
Example:
Hydrogen atom has one electron in its outermost shell. Two hydrogen atoms combine through a single covalent bond in which each atom equally contributes one electron in a mutually shared electron pair.
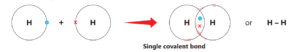
5. Electronic configuration
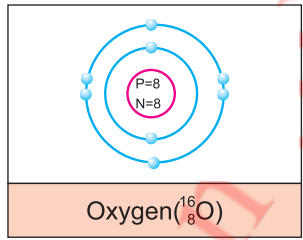
Arrangement of electrons around the nucleus of an atom is called electronic configuration.
Example: Oxygen atom have 8 electrons. Two electrons are in 1st Shall and six electrons are in 2nd Shall.
6.3 Answer the following questions.
1. Write the symbols for the following:
Copper, iron, chlorine, potassium, argon, phosphorus, beryllium, carbon, calcium, silicon.
| Elements | Symbol |
| Copper | Cu |
| Iron | Fe |
| Chlorine | Cl |
| Potassium | K |
| Argon | Ar |
| Phosphorus | P |
| Beryllium | Be |
| Carbon | C |
| Calcium | Ca |
| Silicon | Si |
2. Write the chemical formulae of the following:
Sodium bicarbonate, calcium hydroxide, ammonia, potassium chloride, acetic acid, ammonium hydroxide, sulphuric acid, nitric acid, benzene, methane.
| Compounds | Formulae |
| Sodium bicarbonate | NaHCO3 |
| Calcium hydroxide | CaOH |
| Ammonia | NH3 |
| Potassium chloride | KCl |
| Acetic acid | CH3COOH |
| Ammonium hydroxide | NH4OH |
| Sulphuric acid | H2SO4 |
| Nitric acid | HNO3 |
| Benzene | C6H6 |
| Methane | CH4 |
3. In what way the molecule of an element is different from that of a compound?
Molecule of an element consists of only one type of atom chemically bonded together. All the atoms in the molecule are of the same element. For example Oxygen (O2), Hydrogen (H2), Ozone (O3).
On other hand molecule of an compound consists of two or more different types of atoms chemically bonded together. The atoms come from different elements in fixed ratios. For example Water (H2), Sodium Chloride (NaCl)
4. State the number and kinds of atoms present in carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)?
Carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) composed of one atom of carbon and four atoms of chlorine.
5. Differentiate the following
(a) Symbol and formula
Symbol
A symbol is a representation of a single element. It consists of one or two letters derived from the element’s name, usually in Latin or English.
Examples:
• Hydrogen: H
• Oxygen: O
• Sodium: Na (from its Latin name Natrium).
formula
A symbolic representation of one molecule of an element or a compound is called its formula.
Example: H2O is the chemical formula of water. It 2 shows that each molecule of water contains two atoms of hydrogen and one atom of oxygen chemically combined together.
(b) Positive ion and negative ion.
Positive Ion
When an atom loses electron(s), it become positively charged. The positively charged atoms or group of atoms termed as cation. For example sodium ion Na+.
Negative Ion
When an atom gains electron(s), it become negatively charged. The negatively charged atoms or group of atoms termed as anion. For example sodium ion Cl–.
6.4 Investigate the metallic bond.
Metallic bonding is a type of chemical bonding that arises from the electrostatic attractive force between conduction electrons and positively charged metal ions. It may be described as the sharing of free electrons among a structure of positively charged ions.