UNIT NO.5
Physical and Chemical Changes
(Solved Exercise)
5.1 Select one or more answers as indicated?
(i) Three of the following are alike. Select the one that is different from the others.
a.Solubility b.Conductance c.Oxidation d.Boiling of a substance
(ii) A physical change occurs when:
a.Iron rusts b.Solution of common salt is heated
c.A piece of wood burns d.Sugar is heated strongly
(iii) A gas produced on heating solid potassium chlorate is:
a.Hydrogen b.Carbon dioxide c.Methane d.Oxygen
(iv) Select all that happen during a chemical change.
a.A temporary change occurs
b.Composition of the substances is changed
c.Properties of the substances are changed
d.New substances with different properties are formed.
(v) Freezing of a liquid is a:
a.Chemical change. b.Chemical property c.Physical change d.None of above.
(vi) What are the products when electric current is passed through water?
a.Only steam b.Hydrogen and steam
c.Hydrogen and oxygen d.Oxygen and steam
(vii) A piece of iron is kept in open air for 5 days. A film of corrosion formed over it is:
a.Iron oxide b.Iron sulphide c.Iron chloride d.Iron hydride
(viii) During combustion, a substance reacts with:
a.Hydrogen b.Water c.Carbon dioxide d.Oxygen
(xi) The temperature at which a liquid’s vapour pressure is equal to the external pressure surrounding the liquid is:
a.Melting point b.Boiling point
c.Freezing point d.Highest temperature
(x) Silver + Hydrogen sulphide + Oxygen → Silver sulphide + water
The above reaction is known as:
a.Combustion b.Rusting c.Tarnishing d.Dehydration
5.2 Define the following:
1. Physical change
A change in the physical properties of a substance is called physical change.
2. Chemical change
A change in chemical properties of a substance is called chemical change.
3. Physical property
Physical properties are due to the physical behaviour of the substances.
4. Chemical property
Chemical properties are associated with the chemical structure of the substance. A change in the chemical properties of a substance is called chemical change or chemical reaction.
5. Melting point
Melting point is the specific temperature for a solid at which, it begins to melt and converts from solid state to liquid state.
OR
A temperature at which, solid state of a substance is in equilibrium with its liquid state at standard pressure is called melting point of that substance. For example, the melting point of water is 0 °C.
6. Freezing point
Freezing point is the specific temperature for a liquid at which, it begins to freeze and converts from liquid state to solid state.
7. Boiling point
Boiling point is the specific temperature for a liquid at which, it begins to boil and converts from liquid state to gaseous state.
OR
The temperature at which, the vapor pressure of a liquid becomes equal to the atmospheric pressure is called boiling point of that liquid. For example the boiling point of water is 100 °C.
8. Solubility
The Solubility of a substance in a solvent (usually liquid) is the maximum amount of that substance which can be dissolved in 100 gram of the solvent at particular temperature and pressure.
9. Rusting
Rusting is a chemical change during which oxygen in the moist air reacts with the iron (Fe) to convert it into iron oxide (rust):
Fe + O2(moist air) → Fe2O3
10. Tarnishing
Chemical reaction of oxygen with other substances is called oxidation. Tarnishing is also an example of oxidation. Tarnish is a thin film of corrosion that forms on the surface of the objects made of silver, copper, brass, aluminium, magnesium, etc.
5.3 Complete the following:
(a) Hydrogen + Oxygen → Water
(b) Carbon + Oxygen → Carbon dioxide
(c) Methane + Oxygen → Carbon dioxide + Water
(d) Nitrogen + Hydrogen → Ammonia
(e) Iron + Sulphur → Iron Sulfide
5.4 Answer the following questions.
1. What are physical changes? Explain with examples.
A change in the physical properties of a substance is called physical change. Physical change is a temporary change. The form of a substance appears as the result of a physical change can be reversed into its original form by a simple physical method. For example, water on freezing changes into ice, which can be reversed to liquid water on heating. Water on heating changes into steam, which can be reversed to liquid water on cooling.
2. Describe role of oxygen in various chemical reactions that occur naturally.
Combustion
When we rub a matchstick on the side of the matchbox, it begins to burn. The process of burning is
called combustion. Combustion is a chemical change which appears when oxygen of the air
reacts with the fuel like coal, etc.
C + O2 → CO2 + Heat
Rusting
Rusting is a chemical change during which oxygen in the moist air reacts with the iron (Fe) to convert it into iron oxide (rust):
Fe + O2(moist air) → Fe2O3
Tarnishing
Chemical reaction of oxygen with other substances is called oxidation. Tarnishing is also an example of oxidation. Tarnish is a thin film of corrosion that forms on the surface of the objects made of silver, copper, brass, aluminium, magnesium, etc.
3. How can we prevent the objects made of iron from rusting?
The objects made of iron are damaged if they are not kept safe from rusting. We can take the following measures to prevent metallic objects from rusting:
Applying oil
Coating a layer of oil on the objects keeps the air and moisture away from them. In this way, the objects remain safe from rusting.
Applying paints
Applying paint on the surface of the objects keeps the air and moisture away from them. In this way, the objects remain safe from rusting.
Forming alloy
Making alloys of iron is a better method to avoid rusting. Stainless steel is an alloy of iron that can be used in many cases.
Dry coating
Applying rust-preventing dry coating is useful in shipping, storage, etc. These coatings dry quickly forming a protective layer on metal parts and equipment.
Proper storage
Proper storage of metal parts and equipment in a dry or low moist area where temperature conditions are not suited to rusting is also a better strategy to avoid rusting.
Galvanizing
Application of protective zinc coating over iron or steel products is called galvanizing. It is an excellent rust barrier.
Coat powder
A solid powder of acrylic, vinyl, epoxy, etc., is used to keep the moisture away from the metal object. In this way rusting can be avoided.
4. Describe the uses of materials with respect to their physical properties.
Conductivity, solubility, freezing point, boiling point, etc., are the physical properties of the
materials due to which they are used for various purposes in life.
Conductivity
Conductivity is a physical property of metals to conduct electric current through them. Metallic wire, e.g., copper wire is spread in electric wirings in our homes, schools, industries and where the electricity is required. In this way, the conductivity of copper is used for making use of electricity in almost every walk of life.
Solubility
Water is an excellent solvent. Due to this property, water dissolves digested food and facilitates its passage into blood through walls of the intestines. Most of the medicines are dissolved in water to be injected into blood. Nutrients in soil are dissolved in water for their diffusion into roots.
Freezing point
Milk, milk products and other food items are freeze at their freezing points to increase their shelf life. A variety of medicines is kept at freezing points to store them for long time.
Boiling point
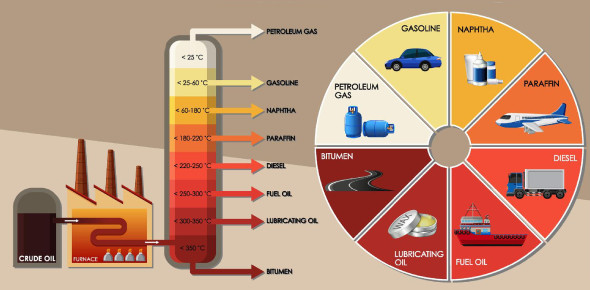
During fractional distillation of crude oil, different components (natural gas, petrol, diesel, etc.) are separated at their boiling points.
5. Describe the uses of materials with respect to their chemical properties.
Reactivity, flammability, acidity, etc., are the chemical properties of the materials due to which they are used in preparing useful products.
Reactivity
Reactivity is the tendency of substance to under go chemical reactions. Decomposition of baking powder on heating produces carbon dioxide. Due to this property, baking powder is used in the materials of bakery products (bread, etc.). Carbon dioxide produced from baking powder on heating makes the products (bread, etc.) porous, soft and fluffy.
Acidity
Acidity in stomach produced due to hydrochloric acid in gastric juice is used in digestion of food. Acidity produced by acidity regulators helps to preserve the original taste and colour of food products. It also prevents the growth of dangerous microorganisms in preserved food products.
Flammability
Flammability is the ability of substances to burn. Burning of acetylene with oxygen produces a high temperature flame used for welding and cutting of metals.
5.5 Constructed Response Questions
1. The gas we use in our kitchen is mostly methane.
(a) What are the reactants when we burn methane is burnt?
In this reaction Methane and Oxygen are reactants.
(b) What are the products when we burn methane is burnt?
Carbon dioxide gas and water with heat are products.
(c) Write the word equation for burning of methane.
Methane + Oxygen → Carbon dioxide + Water
2. Wet clothes are hanged in the sun and they become dry.
(a) What happens to the water in wet clothes?
In this process water evaporates.
(b) What makes its removal from the clothes?
Evaporation process makes its removal from the clothes
(c) Is this a chemical change?
No. It is not chemical change. It is physical change.
(d) Name the process involved in this change
Evaporation process involved in this change.
3. Observe the phenomena given in Figure and answer the following questions.
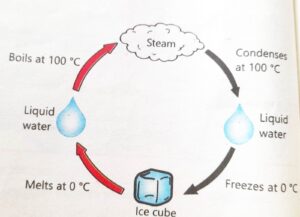
(a) Point out the changes being happened.
Physical change being happened.
(b) Identify the chemical changes occurring therein.
There is no chemical change occur.
(c) Identify the physical changes occurring therein.
Condensation, Freezing, Melting, Boiling
(d) Name the processes involved in the whole phenomena.
Condensation process, Freezing process, Melting process, Boiling process.
5.6 Investigate the role of boiling points of different components of crude oil in their
separation during fractional distillation of crude oil.
The crude oil is refined in oil refineries. It is carried out by the process of fractional distillation. Components of crude oil is separated on the basis of boiling points.
Crude oil is heated under pressure and temperature 400°C. The vapours of crude oil are passed through a tower from near its bottom. These vapours rise up and the components of crude oil got separated at different points according to their boiling points.