UNIT NO.1
Plant System
(Solved Exercise)
1.2 Give short answers.
1. What is primary root?
The initial root which grows from radical of the embryo is the primary root.
2. What is secondary root?
The branch of root which grows from primary root is called secondary root.
3. State the function of root cap.
It protects the newly born soft cells from being damaged and environmental stresses.
4. Write word equation for photosynthesis.
Carbon dioxide + Water + Sunlight energy → Food (Glucose) + Oxygen
5. Write word equation for respiration.
Food (Glucose) + Oxygen → Carbon dioxide + Water + Chemical energy
1.3 Differentiate between:
1. Root system and shoot system
Root system
Roots are the underground parts of the plants forming a system specialized for absorption of water and nutrients from the soil is called Root System.
Shoot system
The areal parts of the plants such as stem, its branches, leaves, flowers and fruit, etc., specialized for different functions make the shoot system.
2. Xylem and phloem
Xylem
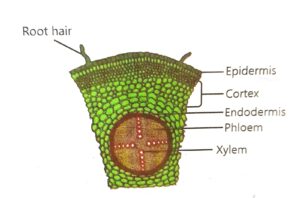
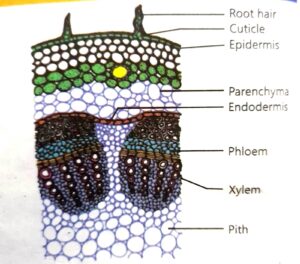
Xylem conducts water from roots to leaves through stem.
Phloem
Phloem transports food from leaves to roots and other parts of the plants.
3. Diffusion and osmosis
Diffusion
Movement of material particles from the area where they are more to the area where they are less is called diffusion.
Osmosis
The diffusion through membranes (like cell membranes) is called osmosis.
4. Epidermis and endodermis
Epidermis
Epidermis is an outermost layer of thin walled cells. It provides protection.
Endodermis
The innermost layer of cortex which consists of barrel shaped cells is called endodermis. It regulates the movement of water and hormones, etc., into and out of the vascular system.
5. Transpiration and evaporation
Transpiration
The loss of water from aerial parts of the plants is called transpiration.
Evaporation
Evaporation is the process in which a liquid, such as water, transforms into a gas or vapor due to heat energy, without reaching its boiling point.
6. Capillary action and transpiration pull
Capillary action
Very narrow glass tubes are called capillary tubes. Water moves up in the capillary tubes due to interaction between water molecules and surface of the tubes. This effect is called capillary action.
Transpiration pull
Transpiration pull is the movement of water in plants from roots to leaves, driven by the evaporation of water from the leaf surface, creating a negative pressure gradient that pulls water up through the plant’s vascular system.
1.4 Answer the following questions:
1. Describe the following in plants:
(i) Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is defined as the process during which carbon dioxide and water combine in the presence of sunlight and chlorophyll to form glucose (food) and oxygen.
Carbon dioxide + Water + Sunlight energy → Food (Glucose) + Oxygen
(ii) Respiration
Respiration is defined as the process during which glucose (food) reacts with oxygen to produce
carbon dioxide, water and energy required for survival of life.
Food (Glucose) + Oxygen Carbon → dioxide + Water + Chemical energy
Respiration takes place in all the cells of living bodies. The mitochondria which are found in the cells perform the process of respiration. For this reason, mitochondria are called power house of the cell.
(iii) Transpiration
Plants continuously absorb water from soil through roots. The same is being conducted to leaves where it is used in photosynthesis. The excessive water is removed through stomata and from the aerial parts of the plants. The loss of water from aerial parts of the plants is called transpiration.
2. Draw and label the internal structures of the following:
(i) Root
(ii) Stem
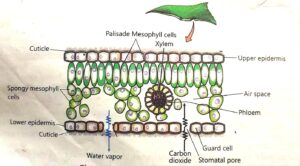
(iii) Leaf
3. Compare and contrast the process of photosynthesis and respiration.
Comparison and Contrast between Photosynthesis and Respiration
1. Photosynthesis takes place in green plants, algae and some bacteria, whereas, respiration takes place in all the living things.
2. Photosynthesis takes place in chloroplasts, whereas, respiration takes place in mitochondria.
3. Photosynthesis uses sunlight energy to prepare food, whereas, respiration releases energy from food which is used for growth and performing all other body functions.
4. The products made during photosynthesis, i.e., glucose and oxygen are the reactants of respiration.
5. The products of respiration, i.e., carbon dioxide and water are the reactants of photosynthesis.
4. Describe the factors affecting the rate of transpiration.
Factors Affecting the Rate of Transpiration
Wind, temperature, light and humidity are the main factors that affect the rate of transpiration.
Wind
The still air surrounding the plant leaves becomes humid and resists the diffusion of water from leaves into the air. It decreases the rate of transpiration. Wind sweeps the humidity away from leaves surroundings and increases the rate of transpiration.
Temperature
Rise in temperature provides more energy to the water molecules for evaporation from the leaves surfaces, hence, increases the rate of transpiration.
Light
In sunlight, the stomata remain open for removal of water through them. At night stomata are closed. In this way light also affects the rate of transpiration.
Humidity
Humid air surrounding the plants contains more amount of water, thus, decreasing the rate of diffusion of water molecules from plants leaves into air. It slows down the transpiration. The rate of transpiration is rapid in dry air.
5. Describe the importance of vascular bundles in plants.
Xylem and phloem form vascular bundle. Main function of vascular bundle is transport food and water in plants. Xylem conducts water and minerals absorbed from roots to leaves through stem. Phloem transports food from leaves to roots and other parts of the plants.
1.5 Constructed Response Questions
1. Photosynthesis does not take place in animals but it is beneficial for animals also. How?
Photosynthesis produces oxygen, which animals need for respiration. It also provides food sources for herbivores and creates habitats for animals.
2. Plants produce food and oxygen during photosynthesis, which does not take place at night. Where do plants get oxygen from for respiration at night?
Plants get some oxygen from the air for respiration at night, but the majority of the oxygen used for respiration during the night comes from the breakdown of stored food which produced by photosynthesis at day time.
3. Why should not we sleep under tree at night?
At night time tree release carbon dioxide during respiration process. Due to excess amount of carbon dioxide, sleeping under trees at night can be unsafe.
4. How the structure of leaf is adapted to the process of photosynthesis?
1. The blades of leaves are flat and absorb maximum light required for photosynthesis.
2. Thin blades of leaves make the light and carbon dioxide reach the internal parts easily.
3. Thick layer of palisade mesophyll containing large number of chloroplasts just beneath the upper epidermis can make maximum absorption of light to make food for the plant.
4. Maximum air spaces among spongy mesophyll near the lower epidermis provide an easy passage for carbon dioxide to diffuse into cells containing chloroplasts to facilitate photosynthesis.
5. Numerous stomata in the lower epidermis absorb maximum carbon dioxide from the air needed for photosynthesis.
6. Division of vascular bundles into small branches spread throughout the leaf makes an easy and maximum water supply needed for photosynthesis.
5. Why is transpiration important for plants?
Transpiration pulls the water through air spaces in spongy mesophyll and keeps the mesophyll moist, which is essential for the exchange of gases. Effects of evaporation of water from leaves or stems are:
• cools the surface of the leaves and the surroundings as well,
• allows the movement of minerals from the soil to different parts of the plant,
• helps in growth and development.
• controls the temperature of the plants.
6. Describe the role of magnesium and nitrogen in plants nutrition.
Magnesium
Magnesium is required by plants for the formation of chlorophyll. It is helpful for the functioning of enzymes to produce carbohydrates and fats. Its deficiency causes poor growth, yellowing and wilting of leaves.
Nitrogen
Nitrogen in the form of its compounds, (nitrates) dissolved in soil water, is required by plants for making chlorophyll and amino acids. Amino acids form proteins. Chlorophyll is necessary for photosynthesis. Proteins are necessary for growth, repair and other developments and defensive functions. Deficiency in nitrogen makes the leaves pale green or yellow. It affects the rate of photosynthesis and growth in plants.
7. Explore the natural raise of water based on the principle of transpiration.
Transpiration, the process by which plants release water vapor through their leaves, creates a suction force. This force pulls water from the roots up through the plant’s vascular system. As water molecules evaporate from the leaves, more water is drawn up from the roots to replace it, resulting in the natural rise of water within the plant.
1.6 Investigate:
(i) Function of the following in plants:
(a) Root hairs
Root hairs provide the surface area for absorption of water.
(b) Stomata
Stomata allow exchange of carbon dioxide and oxygen. They also diffuse out water vapour.
(c) Spongy mesophyll
Spongy mesophyll having air space among them which provide a large surface area for the diffusion of gases to facilitate photosynthesis process.
(ii) Internal structure and functions of the following in plants:
(a) root (b) stem (c) leaf
(a) Root:
- Internal structure: Roots consist of various layers, including the epidermis, cortex, endodermis, pericycle, and vascular tissue (xylem and phloem).
- Functions: Roots anchor the plant in the soil, absorb water and minerals, store nutrients, and provide support.
(b) Stem:
- Internal structure: Stems contain vascular bundles surrounded by ground tissue, with an outer layer of epidermis.
- Functions: Stems provide structural support, transport water, nutrients, and food between roots and leaves.
(c) Leaf:
- Internal structure: Leaves are composed of upper and lower epidermis, mesophyll (palisade and spongy layers), vascular bundles, and stomata.
- Functions: Leaves are the primary sites of photosynthesis, where they absorb light energy, exchange gases (carbon dioxide and oxygen), regulate water loss through transpiration and prepared food with oxygen.