UNIT NO.1
Cellular Organization
(Solved Exercise)
1.1 Encircle the correct option.
1.2 Give the short answers.
- Name the cell organelle that control the whole cell activity.
Nucleus controls the the whole cell activity. - Write the function of blood in human body.
Blood circulates throughout the body to transport different materials from one part of the body to another. - Enlist the organs involved in blood circulatory system in man.
i. Heart
ii. blood vessels
iii. Lungs - Name the red coloured pigment present in red blood cell.
Haemogloban is the red coloured pigment present in red blood cell.
1.3 Differentiate between
- Animal cell and Plant cell
Plant Cell
1. Outermost covering of plant cell is cell wall.
2. A large vacuole is present in plant cell.
3. Plant cells have chloroplast containing green pigment called chlorophyll.
4. Centrioles are not found in plant call.Animal Cell
1. Outermost part of animal cell is cell membrane.
2. Many small vacuoles are present in animal cell.
3. Animal cells have no chloroplast.
4. Centrioles are present in animal cell. - Cytoplasm and Nucleoplasm
Cytoplasm
1. The content of the cell covers by cell membrane is called cytoplasm.
2. It is a semi-viscous material that consists of water, salts and proteins etc.
3. Most of cell functions take place in cytoplasm.
Nucleoplasm
1. The material inside the nucleus is called nucleoplasm.
2. Nucleoplasm contains thread like structure called chromosomes.
3. Chromosomes are made up of DNA and proteins.
- Xylem and Phloem
Xylem
1. Xylem tissue is formed by xylem cells.
2. Xylem tissue conducts water from roots to leaves.Phloem
1. Phloem tissue is formed by phloem cells.
2. Phloem tissue transports food from leaves to other parts of the plant. - Epidermis tissue and Epithelial tissue
Epidermal Tissue
1. Epidermal tissue is formed by epidermis cells.
2. Epidermis tissue present in plants.
3. Epidermis tissue makes outer protective layer in roots, stem and leaves of plants.Epithelial Tissue
1. Epithelial tissue consists of epithelial cells.
2. Epithelial tissue present in animals.
3. Epithelial tissue makes the surface layer of skin. - Root system and Shoot system in plants
Root System
1. Roots and its branches make root system in plants.
2. It absorbs water and nutrients from the soil.Shoot System
1. Stem, its branches and flowers make the shoot system in the plant.
2. It supports the whole plant structure.
1.4 Constructed response questions
- Relate the structure of the following with the function they perform.
(a) Cell Wall
Cell wall makes outer covering of the cells of plants , algae, fungi and bacteria. Rigid layered structure of the cell wall is closely related to the functions it performs, which include maintaining cell shape, providing mechanical strength and protection.
(b) Nerve Cells
Nerve cells or neurons are long and branched. This structure enables neurons to rapidly send message from one part of the body to another.
(c) Xylem
Xylem cells are tubular in shape. This structure enables them to conduct water and dissolved minerals from roots to the rest of the plant.
(d) Phloem
Phloem cells are tubular in shape. This structure enables them to transport food from leaves to other parts of plans.
(e) Vacuole in plant cell
Vacuoles in plant cell is a large organelle that filled with water and many other substances. This structure of vacuole helps to maintain the shape of plant cell.
2. Identify the organization of man tissue in the following and state there functions.
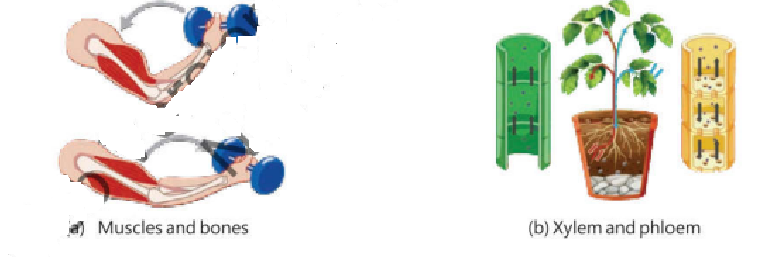
(a) Muscles and bones
Skeletal Muscle Tissue: It cause movement in bones.
Bone Tissue: It gives shape and provide support to body parts.
(b) Xylem and Phloem
Xylem Tissue: It conducts water from roots to leaves of plants.
Phloem Tissue: It transports food from leaves to parts of the plants.
1.5 Investigate
- Function of muscle tissue in:
(a) Heart : Cardiac muscle tissue in the heart makes the heart beat to pump blood for its circulation in the body.
(b) Stomach : Smooth muscle tissue inside the stomach cause movement in stomach to digest the food.
(c) Eye : Smooth muscle tissue present in eye lid cause blinking of eye.
2. Structure and function of the following in plants:
(a) Epidermal tissue : Outer protective layer in roots, stem and leaves of plants is called epidermis. It is formed by tile-like cells, which are joined together to form single layered tissue called epidermis. The cells forming epidermal tissue are called epidermal cells.
(b) Mesophyll tissue : Mesophyll tissue is also called photosynthetic tissue. It is specialized to prepare food and remove wastes. It is located between upper and lower epidermal layers in the leaves. Cells forming mesophyll tissue are called mesophyll cells. Palisade mesophyll cells are elongated and tightly packed together forming a layer beneath the upper epidermis. These cells are rich in chloroplasts and prepare food during photosynthesis. Spongy mesophyll cells are loosely arranged with air spaces among them. Spongy mesophyll is located below the palisade layer and above the lower epidermis. Photosynthesis also takes place in spongy mesophyll cells.
(c) Chloroplast : Plant cells have chloroplasts containing green pigment called chlorophyll. This is the reason that the parts of the plants with chloroplasts in their cells look green. Chlorophyll absorbs energy from sunlight which is used in photosynthesis for production of food. Chloroplasts are thus called food producers in plant cells. Chloroplasts are not present in animal cells.